
Node with a hidden subgraph
![[Contents]](../buttons/over.gif)
![[Intro]](../buttons/intro.gif)
![[Reference]](../buttons/ref.gif)
![[Tutorial]](../buttons/tut.gif)

![[Index]](../buttons/index.gif)
Scaling is a feature to reduce the size of a probably large graph visualization for getting an overview. In a scaled graph, some details are dropped (e.g. the text of nodes is not drawn), but all the other interactions are still available. So for example, you can even use fine tuning in a scaled drawing of a graph. One way to reduce the scale is by selecting menu View/Fit Scale to Window. Do this right now! A new (maximal) scale is calculated and set such that the graph is completely visible in the base window. Of course, this modifies the scale only if the graph is larger than the base window.
Now open the
scale dialog by using
menu
View/Scale.... In this
window you can set the scale to any rate between 1% and 100%. Simply
move the slider to some arbitrary values and observe the effect on the
visualization. Pressing button Fit to Window in the dialog is the
same as selecting the menu you have just used before. You cannot magnify
the graph this way (i.e. there is no scale >100%), but you can use a larger
font for magnification as it is discussed in the previous tutorial section.
Before going to the next
exercise, set the scale back to 100% (there are different ways to do
so, for example by clicking on the Large label in the scale dialog)
and afterwards finish the dialog by pressing the Close push button.
Using Abstractions to simplify a Layout
Interactive abstractions are used to hide particular parts of a graph that
may be uninteresting or confusing. Abstractions are temporary operations
that can be undone at any time. Select some node in the graph that has
at least one child node. Now you can fade out the subgraph of this node
by selecting menu
Abstraction/Hide Subgraph.
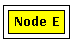
After doing so, the children of the node are removed from the visualization
and the selected node is drawn with an icon showing a pair of scissors
to emphasize the applied abstraction:

Another abstraction is hiding all the edges of a selected node: Both the incoming (from the parent nodes) and the outgoing edges (to the child nodes). The three operations for edge abstractions are also available in the Abstraction menu. After hiding the edges of a selected node, they are removed from the graph visualization and the node is drawn with a rectangular border to emphasize the applied abstraction:
A very useful feature is the navigator dialog which appears after using menu Navigation/Navigator.... Select exactly one node in the graph and press one of the four arrow buttons of the navigator dialog to go to the next node in the corresponding direction. This way you can easily browse a graph by hopping from node to node. The speed of animation, used for scrolling to the new focus point, can be adjusted with menu Options/General Settings.... You can also use the cursor keys of the keyboard to trigger navigation, so usually you do not need the navigator dialog. Check button Structural Navigation is explained on the navigator dialog help page of the user interface documentation.
Finally we will search for nodes with a specified text by using the find dialog. Select menu Navigation/Find... to pop up this window. Now enter the substring you are looking for in the Find field. If you have loaded file graph_example.daVinci, then for example type a 6 and press the Find push button afterwards. This will search for a node with a text containing the 6. Press Find again to go to the next match.
After playing a little bit with these features, close both the find- and navigator dialog by selecting the Close button, if not already done.