
| Home |
| uDraw(Graph) |
| Download |
| Service & Support |
| Legal |
How to connect an Application to the API
From a technical point of view, communication between uDraw(Graph) and a connected application program is performed with two pipes. One is used to send commands to the uDraw(Graph) API, e.g. to transmit graphs, to attach menus/icons or to call menu functions. The other one is used to receive the answers, e.g. return values, user events, etc. Alternatively, bi-directional TCP/IP socket communication can be used where uDraw(Graph) acts as a socket server and the application program is a socket client. The following figure illustrates this approach:
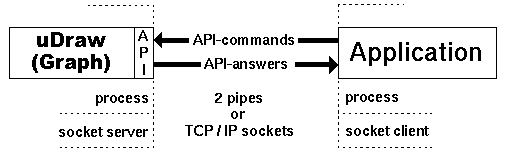
Types of API communication
Only one application program can be connected with uDraw(Graph) at a time,
but this client process is able to visualize many graphs in different
windows at a time, see
Communication with Pipes
Choose which way to go
There are two options for connecting an application to the API with pipes. Either uDraw(Graph) is doing this job, which is the easiest way, or the application connects uDraw(Graph) in order to have more flexibility. The point is whether uDraw(Graph) or the application is the parent process. The advantage of the first solution where uDraw(Graph) is responsible for establishing connection is that the application programmer does not have to deal with process and pipe programming. In this case, all an application program has to do is sending commands to the API by printing on the standard output ("stdout") and receiving the answers from the API by reading from "stdin". Further, if uDraw(Graph) has launched the application process, the user will be able to disconnect the application later in order to connect another one.
The disadvantage of this solution is that the application's "stdin"
and "stdout" have to be exclusively reserved for communication with
uDraw(Graph).
If more flexibility is needed, e.g. to use other file descriptors
than "stdin" and "stdout", then the application has to establish
the communication with uDraw(Graph) on its own,
Either uDraw(Graph) connects the Application...
uDraw(Graph) is able to connect an application program at start-up time
using command-line option
When the connection has been performed by uDraw(Graph), the user is
able to shutdown the currently connected application at any time
using menu
... or the Application connects uDraw(Graph)
The application program has to start uDraw(Graph) on its own when the
more comfortable method of connection
(
-
Forking a new process
This is the child process used for uDraw(Graph). -
Creating two pipes
One to send commands and the other one to receive answers from the API. -
Redirecting the file descriptors
"stdin" and "stdout" of the new child process (uDraw(Graph)) have to be connected with one side of both pipes. The parent process (application) has to connect two free file descriptors to the other end of both pipes. -
Start uDraw(Graph)
Execute uDraw(Graph) with command-line option-pipe in the forked child process.
Note: the application has to set line-buffered I/O before starting communication with uDraw(Graph) via pipes. For example, in "C" it can be done this way:
| Setting line-buffered I/O |
|---|
| setvbuf(stdin,NULL,_IOLBF,0); setvbuf(stdout,NULL,_IOLBF,0); |
After establishing connection, uDraw(Graph) sends an initial
Communication with TCP/IP Sockets
A more flexible way of communication is to use TCP/IP sockets
instead of pipes.
This way it is even possible to start uDraw(Graph) and the application
program on different computers in a network or even at different
sites.
Please read the
uDraw(Graph) operating in Socket Server Mode
With socket communication, uDraw(Graph) always acts as the socket server
that listens on a specified port for connection requests from an
application.
Initiating the socket server mode can be done either at start-up
time using command-line option
After entering the socket server mode, uDraw(Graph) listens on the
specified port until a socket connection request is received from
an application program.
Then the application is connected to the API and subsequent
connection requests from other applications are ignored unless the
connected application disconnects, because only one application
can be connected to the API at a time.
After the application has disconnected, uDraw(Graph) will automatically
start listening again for connection requests when the command-line
option
If a port ("old") has been specified with option
Starting the Application as a Socket Client
An application program can be connected to the API as a socket
client in two ways.
One option is to simply execute the application program stand-alone
after uDraw(Graph) has been started with command-line option
In both cases, the application has to set up the communication by connecting to the uDraw(Graph) socket port as client. The way this can be done depends on the implementation language and libraries used for the application. Please consult your documentation and programming manuals for details or search for socket programming tutorials in the Internet. Example code for establishing socket communication with uDraw(Graph) is provided in the distribution, look under "simpleclient" in directory "samples".
You can test the socket communication using the
| uDrawGraph(.exe) -server |
| grapheditor(.exe) -client |
This will connect the graph editor application to uDraw(Graph) using sockets. Both programs can even be executed on different computers that are connected by a network.
Testing API Transmission
After establishing a connection for the first time between your
application and uDraw(Graph), you should test the transmission by
sending command
Note: API commands must not have newline or return characters inside. They must have exactly one newline at the end of the command. No other characters, even no spaces must follow this concluding return, except of the next complete command. If these restrictions are not considered, communication with the API will likely fail.